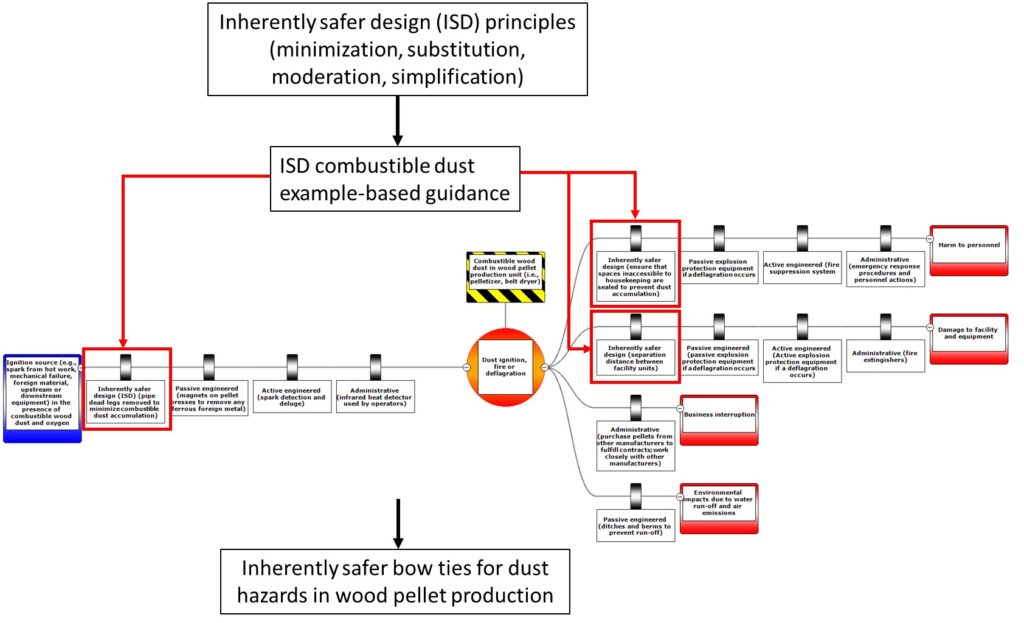
ISD focuses on elimination of hazards and treatment of hazards at the source, rather than relying on only add-on equipment and procedures. ISD is based on four principles: minimization, substitution, moderation, and simplification.
Practical examples of ISD in wood processing plants include:
- Remove unnecessary or hazardous equipment, like fans (minimization).
- Substitute equipment components (e.g., shaft) to prevent failure and ignition source (substitution).
- Relocate hazardous equipment, like cyclones, outside and away from personnel (moderation).
- Relocate fibre storage away from air intake screen for dryer (moderation).
- Consider human factors—use an HMI (human-machine interface) system that clearly indicates status (simplification).
Why ISD?
Considering ISD within process safety management (PSM) helps to prevent and mitigate incidents like dust fires and explosions. Effective risk reduction involves implementation of ISD, engineered equipment, and procedural measures. ISD helps to make processes safer and more robust. There is evidence that ISD may make plants more economical through reduced risk, capital cost, and requirements associated with more complex risk management controls. ISD also supports continuous improvement.
How to Incorporate ISD
ISD can be considered during hazard analysis, incident investigation, and management of change. It can be integrated using example-based guidance, ISD checklist questions, and ISD workshops. An extensive collection of example-based guidance has been developed through research funded by a WorkSafeBC Innovation at Work (now Applied Innovation) grant.
The project team gratefully acknowledges funding from WorkSafeBC under an Innovation at Work 2020 grant for the project “Inherently Safer Bow Ties for Dust Hazard Analysis.” The views, findings, opinions, and conclusions expressed herein do not represent the views of WorkSafeBC.
Resources
Watch webinar: Safety huddle webinar and presentation slides
Read report and fact sheet: Inherently Safer Design in Wood Pellet Production
Read ACS Omega Journal article: Application of Process Hazard Analysis and Inherently Safer Design in Wood Pellet Production
